Actual Cash Outlays for Operating Expenses Are
The cash outlay for income taxes is determined by applying the income tax rate to the cash revenue received less the cash and noncash depreciation expenses. Operating profit can typically be found after operating expenses on the income statement.
Cash Flow Analysis Examples Step By Step Guide
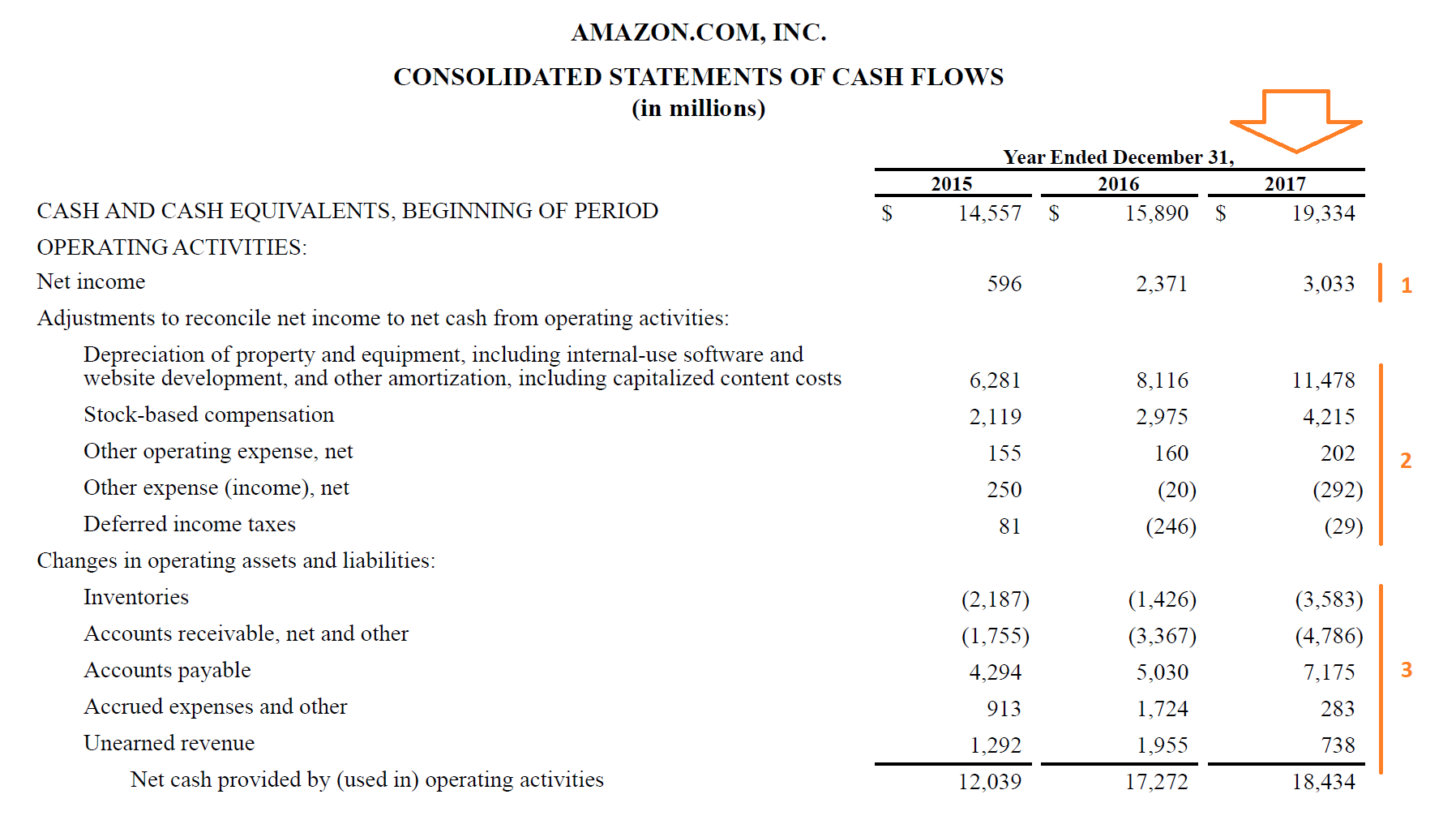
After removing the effect of the acquisition of Datacomm Products and the sale of DTI the increase in Cash Operating Expenses in 1998 was 101.
/dotdash_Final_Cash_Flow_Statement_Analyzing_Cash_Flow_From_Investing_Activities_Jul_2020-01-5297a0ec347e4dd8996f307b3d9d61ad.jpg)
. March 12 2022 Legal fees for drafting a partnership agreement are pre-operating costs. Are patents an operating expense. Operating expenses were about 11 billion in 1987 and are estimated at 61 billion for 1988 and 1989 combined.
They do not represent actual cash flow however. What Are Noncash Expenses. A company may very well have to burn significant cash flow in a given year to build a factory for example but in the years to follow there will be little cash outlays for that plant.
The 176 million operating fund cash earns minimal interest on its Treasury deposits. EBITDA attempts to measure cash flow depreciation and amortization are not actual cash outlays. Operating expenses on the other hand are used for assets that are expected to be purchased and fully utilized within the same fiscal year.
Require an immediate cash outflow in the form of an initial investment in equipment other assets and installation costs. Its also called a cash disbursement or outflow. Cash Operating Expenses from this Sector increased 197 in 1998 after being approximately equal in 1997 and 1996.
This task involves preparing analyses and information that will aid you in determining future monthly amounts for each type of cost expense or payment. Cash Expenditures means all disbursements of cash during a specified Fiscal Year other than distributions to Partners including without limitation payment of operating expenses payment of principal and interest on any Partnership indebtedness other than payments of principal and interest on any Subordinated Loans or Voluntary Loans the. Pre-operating costs include any expenses incurred during the startup or formation of a new businessThey include expenses related to the investigation of a potential new business as well as the actual costs associated with forming or registering the company.
Annual incremental net operating income annual incremental revenue of 250000- annual depreciation of 80000- annual incremental cash operating expense of 100000 70000 Simple rate of return annual incremental net operating income of 70000initial investment of 400000 175. Some costs and expenses will be based on a percentage relationship to sales variable costs expenses while others will be fixed such as building rent and insurance. The most common noncash accounts are for depreciation expenses but others include amortization and bad debt expenses.
Where Is Operating Profit on the Income Statement. T ransactions in noncash expenseaccounts meet the textbook definition of expense. Operating profit on the other hand measures income which will appear lower than EBITDA.
But from the income statement side that cash outlay is spread as an expense over many years rather than just one so that the impact of a large investment doesn. Your net burn rate is the difference between the revenue you take in and your expenses. 3 types of cash flows out.
Both are the result of NCUA assessing federal credit union operating fees in excess of actual expenses in every year since 2015 when the fund equity was just 38 million. The business may spend money on various charges which run the gamut from material costs to selling general and administrative expenses. 3 many projects require periodic outlays for repairs and maintenance and additional operating costs.
Actual cash outlays for salaries advertising and other operating expenses out-of-pocket costs. Companies allocate or amortize the costs over the life of the patent. Proceeds from the sale of farm commodities which continued to reduce total net cash outlays were 23 billion in 1987 and are estimated at 27 billion for 1988 and 1989 combined see pp.
A B C Cash revenue received 92000 452000 222000 Cash operating expenses paid 56000 317000 147000 Depreciation on tax return 14000 32000 22000 Income tax rate 40 30 20 Do not use. A cash outlay is money a company pays for its operating expenses. Office supplies and wages are two examples of operating.
Some require a company to expand its working capital. The indirect method presents the statement of cash flows beginning with net income or loss with subsequent additions to or deductions from that amount for non-cash revenue and expense items resulting in cash flow from operating activities. The cash on hand is almost twice the annual operating expenses.
Generally they decrease owners equity by using up assets. That occurs for example when a federal agency deposits grant funds into recipients accounts or the Social Security Administration disburses payments to beneficiaries. In general outlays occur when a federal agency issues checks disburses cash or makes electronic transfers to liquidate or settle an obligation.
The total-cost approach is the least flexible method for comparing competing projects. The Heartland effect on Cash Operating Expenses was 4317000 in 1998 and 2667000. If you have 10000 of total operating expenses each month your gross burn rate is 10000 because this is your actual cash outlay for operating expenses.
Operating Cash Flow Formula Overview Examples How To Calculate
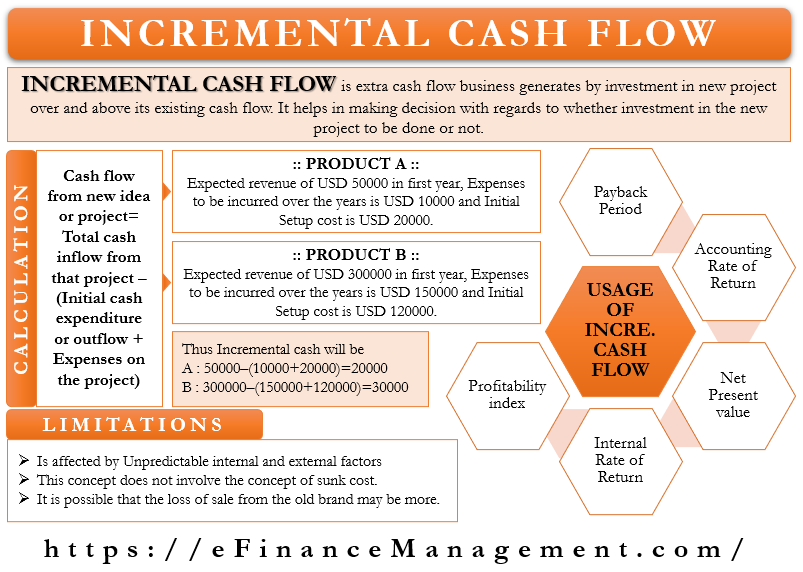
Incremental Cash Flow Meaning Calculation Uses Limitations

Constructing A Capital Budget Ag Decision Maker

Statement Of Cash Flows Ppt Download
/applecfs2019-f5459526c78a46a89131fd59046d7c43.jpg)
Comparing Free Cash Flow Vs Operating Cash Flow
/dotdash_Final_Cash_Flow_Statement_Analyzing_Cash_Flow_From_Investing_Activities_Jul_2020-01-5297a0ec347e4dd8996f307b3d9d61ad.jpg)
Cash Flow Statement Analyzing Cash Flow From Investing Activities

Mcgraw Hill Irwin 16 1 Noncash Expenses Not All Expenses Require Cash Outflows The Most Common Example Is Depreciation Recall That High Country S Proposal Ppt Download
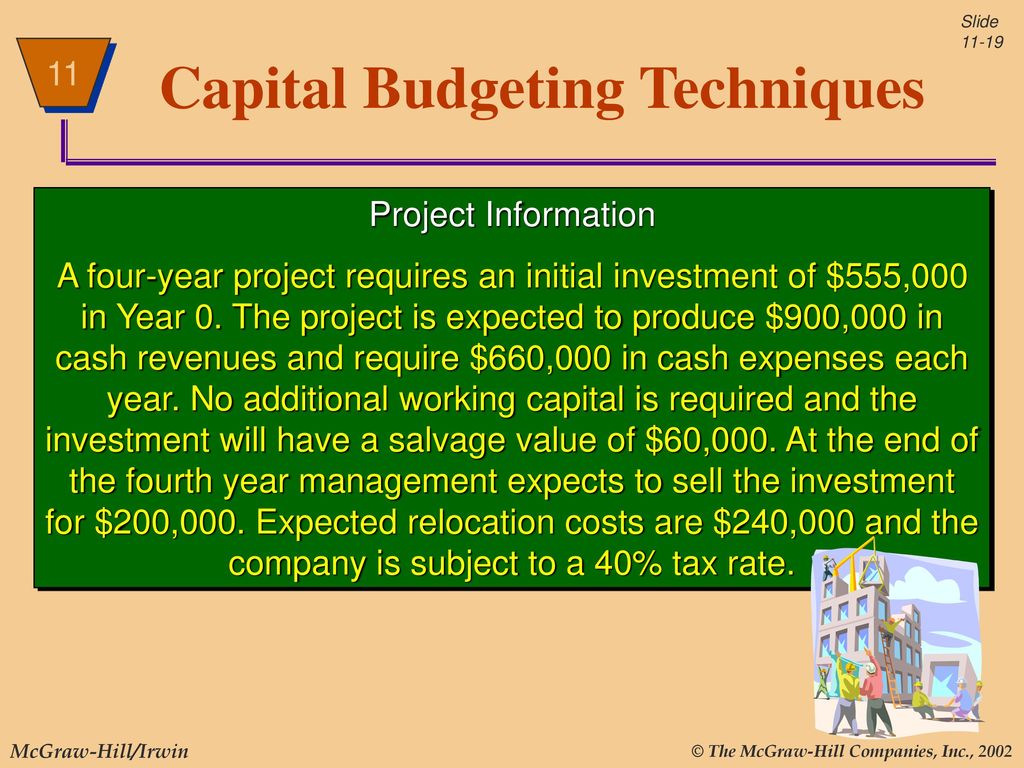
Capital Budgeting Ppt Download

Capital Budgeting Basics Ag Decision Maker
How Do Net Income And Operating Cash Flow Differ
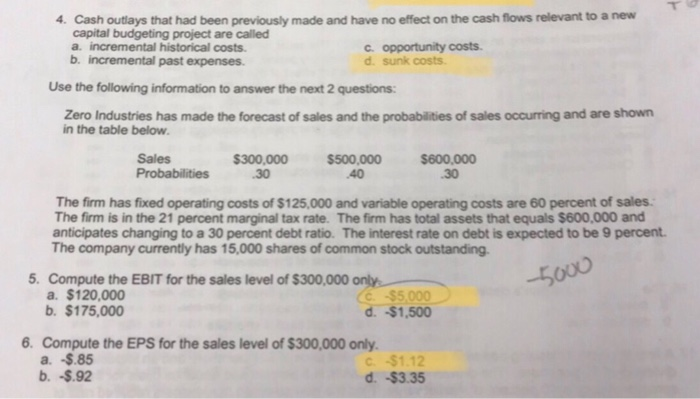
Solved 4 Cash Outlays That Had Been Previously Made And Chegg Com

Capital Budgeting Basics Ag Decision Maker

Constructing A Capital Budget Ag Decision Maker
How Do Net Income And Operating Cash Flow Differ

Capital Budgeting Decisions Chapter Objectives Understand The Nature
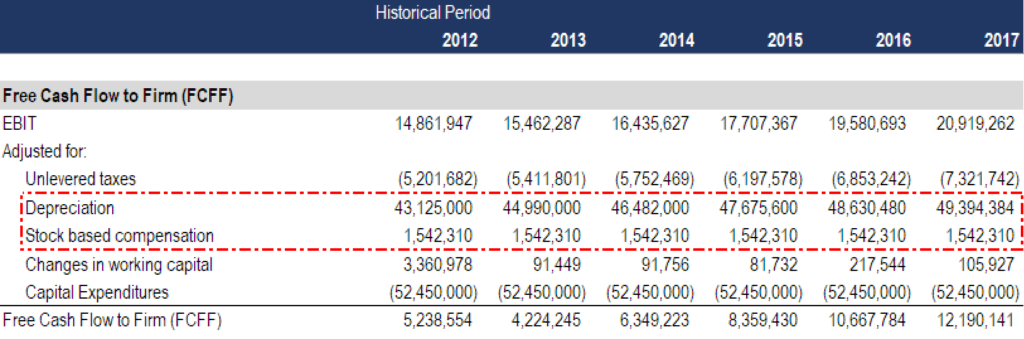
Non Cash Expenses What To Beware Of In Financial Statements
How Do Net Income And Operating Cash Flow Differ

8 1 Capital Budgeting Decisions Part Ii Prepared By Douglas Cloud Pepperdine University Prepared By Douglas Cloud Pepperdine University Ppt Download

Comments
Post a Comment